What is SWIFT in Banking & Payments| A Complete Guide

What is SWIFT & How does It Work?
SWIFT payment System explained in simple words in this video.
In today’s global economy, fast and secure cross-border money transfers are essential. SWIFT, or the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, plays a key role in making this possible. Whether you're a business dealing with international clients or an individual sending money to family abroad, SWIFT money transfers have become the backbone of international financial transactions. This guide will explain what SWIFT money transfer is, how it works, its advantages, and why it matters for international payments.
What is swift in banking
SWIFT money transfer refers to the process of sending money internationally through the SWIFT network.
SWIFT, founded in 1973, is a global messaging network that enables banks and financial institutions to securely send and receive information, such as instructions for transferring money.
It's important to note that SWIFT itself doesn’t hold or transfer funds. Instead, it acts as a secure communication system between banks, ensuring the smooth exchange of messages that facilitate the transfer of money from one country to another.
💡If you want to sell usdt for dirham in UAE you can use EZDEX to find the best online and in person exchange offices and parties.
Who owns SWIFT banking system
SWIFT is a member-owned cooperative based in Belgium. It is not owned by any single individual, corporation, or government.
SWIFT is collectively owned and controlled by its member banks and financial institutions, which use its network to facilitate international payments and financial communications.
Since SWIFT is not owned or controlled by a single country or corporation, it provides a neutral and trusted platform for financial communications.
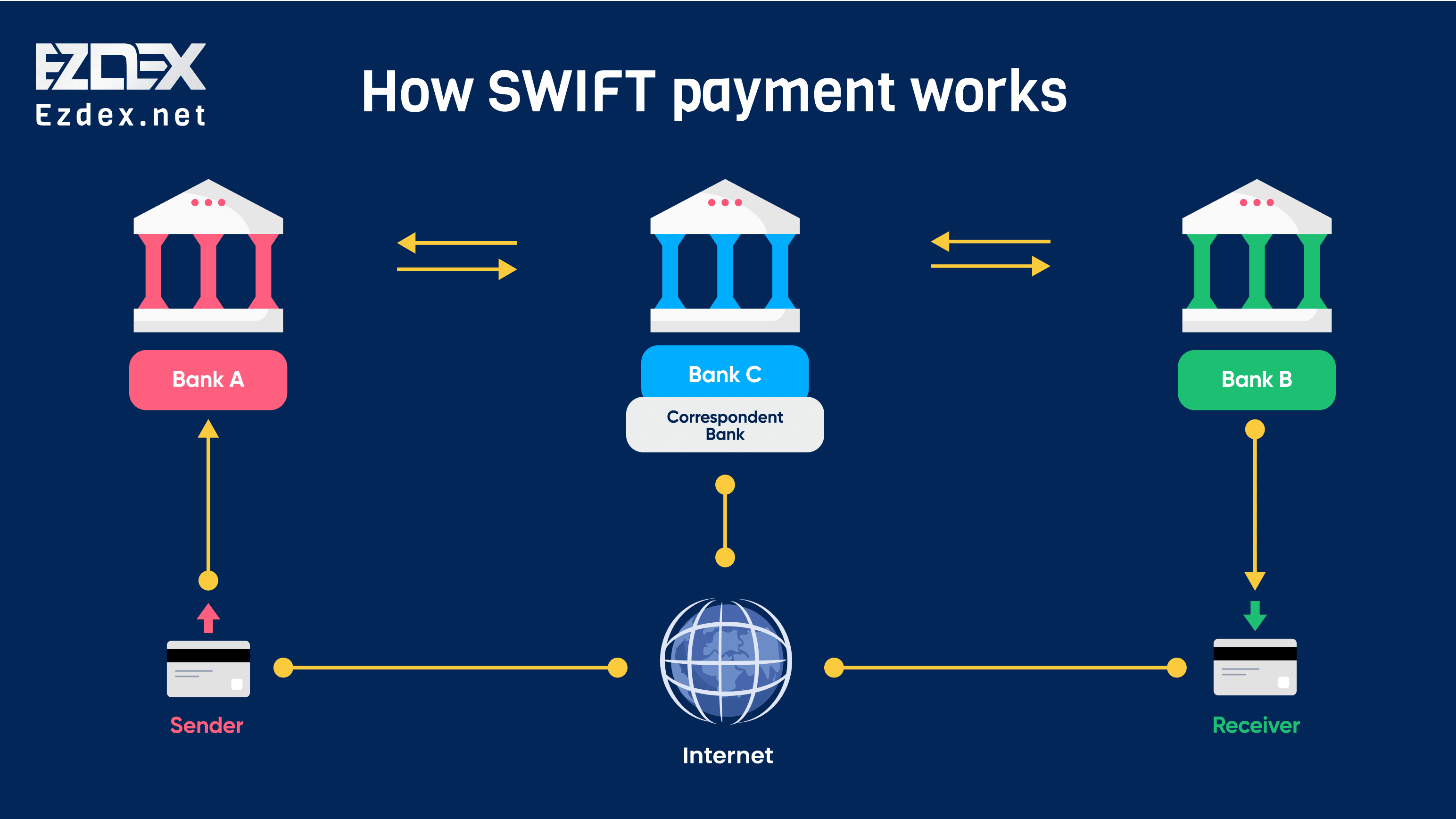
How SWIFT payment works
A SWIFT transfer typically involves multiple financial institutions, especially when sending money across borders. Here’s how it works:
- Sender’s Bank: The sender initiates a transfer through their bank by providing the recipient’s details, including their IBAN (International Bank Account Number) and SWIFT/BIC (Bank Identifier Code). The sender’s bank sends a SWIFT message to the recipient’s bank or an intermediary bank.
- Intermediary Banks: In many cases, intermediary banks facilitate the transfer. This happens when the sender’s and recipient’s banks don’t have a direct relationship. The message passes through one or more intermediary banks, adding processing fees and increasing the time for the transfer.
- Recipient’s Bank: Once the recipient’s bank receives the SWIFT message, they process the payment and credit the money into the recipient's account.
- Transfer Completion: The entire process can take 1-5 business days depending on the banks involved and the countries where the transaction takes place.
Key Benefits of SWIFT Money Transfers
- Reliability: SWIFT has been around for decades and has proven its reliability, making it the trusted choice for international payments.
- Cross-Border Compatibility: SWIFT supports payments in different currencies, ensuring that businesses and individuals can transfer money internationally without currency barriers.
- Wide Acceptance: The SWIFT network is used by virtually every major financial institution in the world, making it easy to send and receive money globally.
- Fast Transfers: While transfers can take up to five days, SWIFT is generally considered fast for international transfers, particularly compared to alternative methods that may take even longer.
🔗Also Read: How long does a SWIFT transfer take?
SWIFT Money Transfer Fees
SWIFT transfers aren’t free. Banks typically charge fees for sending and receiving SWIFT payments. These fees include:
- Sender’s Bank Fees: The bank initiating the SWIFT transfer usually charges a flat fee for the service, ranging from $20 to $50, depending on the bank and the amount being sent.
- Intermediary Bank Fees: If intermediary banks are involved, they may charge processing fees, adding to the overall cost.
- Recipient’s Bank Fees: In some cases, the recipient’s bank may charge a fee to process the incoming transfer.
⚠️It's important to check with your bank for the exact fees before initiating a SWIFT transfer to avoid any surprises.
SWIFT vs. Other Money Transfer Methods
While SWIFT is widely used, it’s not the only way to transfer money internationally. Here's how it compares to other methods:
- SWIFT vs. PayPal: PayPal is faster for small international transfers but tends to have higher currency conversion fees. SWIFT, on the other hand, is better for larger transactions and offers more security.
- SWIFT vs. Wire Transfer: Wire transfers within the same country can be faster and cheaper than SWIFT, but they lack the international reach of SWIFT, which connects thousands of banks globally.
- SWIFT vs. Cryptocurrency: Cryptocurrencies like Tether offer near-instantaneous international transfers but come with volatility and security risks. SWIFT remains more stable and secure for large transactions.
Read the latest news and announcements in this section.
Read the latest tutorials about payment service providers in this section.
You can access full guides and tutorial to use EZDEX services in this section.
Step by step tutorials and photo guides are available in this section.
Access the latest information about financial and economical matters in Turkey in this section.
Access the latest information about financial and economical matters in UAE in this section.
Explore expert guides, tips, and strategies for understanding and working with gold. Learn everything from basics to advanced knowledge.