Blockchain Explained in Simple Words: What Is It and How Does It Work?
You have probably heard about blockchain in recent years. Blockchain technology has gained significant attention across industries, promising to revolutionize everything from finance to supply chain management. However, some of you may still struggle to grasp what blockchain is and how it works. This article provides a comprehensive guide to blockchain technology, explaining its fundamentals, mechanics, and real-world applications.
Table of Contents
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger technology.
It records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring that the data is immutable (cannot be changed) and transparent (visible to all participants within the network). Blockchain is often associated with cryptocurrencies, but its potential applications extend far beyond digital currencies.
Let us take a look to key characteristics of blockchain:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases managed by a central authority, a blockchain is maintained by a network of nodes (computers).
- Immutability: Once information is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered without the consensus of the network.
- Transparency: Every participant in the network has access to the same data, ensuring trust and accountability.
- Security: Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data and transactions.
Check this out: Technical Anlaysis of the Financial Markets PDF
Blockchain & Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain technology forms the backbone of cryptocurrencies, which are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptographic principles to secure transactions.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Tether operate on decentralized networks, eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks. This decentralization not only reduces transaction fees but also empowers users by giving them full control over their funds. Each transaction is recorded on a blockchain, ensuring transparency and preventing fraud.
One of the key benefits of blockchain-powered cryptocurrencies is their ability to enable borderless transactions. Unlike traditional financial systems such as SWIFT, which often involve delays and high costs for cross-border payments, cryptocurrencies allow users to transfer value instantly and at a fraction of the cost. Furthermore, smart contracts—self-executing agreements coded on blockchains like Ethereum—extend the utility of cryptocurrencies by enabling decentralized applications (dApps) and automated processes.
How Does Blockchain Work?
To understand how blockchain works, it’s helpful to break it down into its key components and processes:
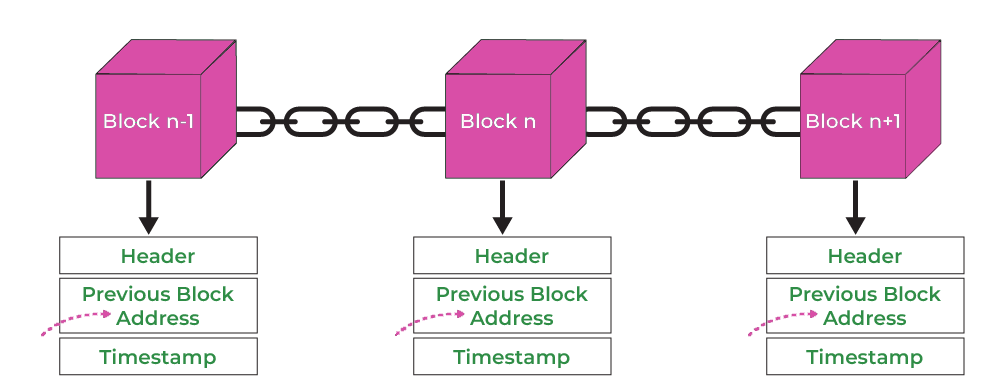
The Structure of a Blockchain
A blockchain is essentially a chain of blocks, where each block contains:
Data: This varies depending on the use case. For example, in cryptocurrencies, the data might include details about transactions.
Hash: A unique identifier that acts like a digital fingerprint for the block. (what is transaction hash/ID)
Previous Block Hash: A reference to the hash of the preceding block, creating a chain.
The Process of Adding Blocks
The process of adding new blocks to a blockchain involves several steps:
- A user initiates a transaction, such as sending Bitcoin to another user.
- The network of nodes validates the transaction to ensure its legitimacy. For example, it checks whether the sender has sufficient funds.
- Validated transactions are grouped together into a block.
- Before the new block can be added to the chain, network participants must agree on its validity (through consensus algorithms).
- Once consensus is achieved, the new block is added to the blockchain, and the transaction is complete.
Decentralization and Distribution
One of blockchain's most important features is its decentralized nature. Instead of being stored on a single server, the ledger is distributed across a network of nodes. This ensures redundancy and makes the system more resilient to attacks or failures.
Cryptography
Blockchain uses cryptography to secure transactions and protect user identities. Public and private keys enable participants to send and receive funds securely, while hashing ensures the integrity of the data.
Types of Blockchains
There are different types of blockchains, each suited to specific use cases:
1. Public Blockchains
Open to anyone who wants to participate.
Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum.
Use Case: Cryptocurrencies, decentralized applications (dApps).
2. Private Blockchains
Restricted to specific participants, often within an organization.
Examples: Hyperledger Fabric.
Use Case: Enterprise solutions, supply chain management.
3. Consortium Blockchains
Controlled by a group of organizations rather than a single entity.
Examples: R3 Corda.
Use Case: Cross-organization collaboration.
4. Hybrid Blockchains
Combine elements of public and private blockchains.
Use Case: Systems requiring both public transparency and private control.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is not limited to cryptocurrencies. Here are some key areas where it is making a difference:
1. Financial Services
Cryptocurrencies: Blockchain’s first and most well-known application is powering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Cross-Border Payments: Blockchain reduces the cost and time associated with international transactions by eliminating intermediaries.
Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts that automatically enforce the terms of an agreement.
2. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain enhances transparency and traceability in supply chains. For example, it allows businesses to verify the authenticity of products, track shipments, and ensure ethical sourcing.
3. Healthcare
Medical Records: Blockchain can store patient data securely and ensure only authorized individuals have access.
Drug Traceability: It can track pharmaceuticals through the supply chain to prevent counterfeit drugs.
4. Voting Systems
Blockchain-based voting systems ensure transparency, security, and trust by preventing tampering and enabling verifiable results.
5. Real Estate
Property Transactions: Blockchain simplifies the process of buying and selling real estate by reducing paperwork and ensuring secure transactions.
Land Registries: It provides a tamper-proof record of property ownership.
6. Identity Management
Blockchain enables secure and decentralized identity solutions, giving users control over their personal information and reducing the risk of identity theft.
Advantages of Blockchain
Blockchain’s cryptographic techniques and decentralization make it highly secure. All participants have access to the same data, reducing the risk of fraud. The tamper-proof nature of blockchain ensures data integrity.
Blockchain eliminates intermediaries, speeding up processes and reducing costs. It focuses on decentralization that removes the need for a central authority, fostering trust among participants.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain
While blockchain has immense potential, it is not without challenges. The most important limitation is scalability. Most blockchains struggle to handle large volumes of transactions quickly.
Energy Consumption is also a challenge. Proof-of-Work blockchains, like Bitcoin, consume significant energy. While implementing blockchain solutions can be technically challenging and require significant expertise.
Final one is the Regulatory Uncertainty. Many governments are still figuring out how to regulate blockchain-based systems.
Future of Blockchain
The future of blockchain is bright, with advancements addressing current limitations and expanding its applications.
More blockchains are adopting energy-efficient consensus mechanisms. Blockchain can enhance the security and functionality of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Also, Businesses across industries are increasingly exploring blockchain for efficiency and innovation.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) based on this technology is now a growing ecosystem of financial services powered by blockchain.
While challenges remain, ongoing innovations and increased adoption suggest that blockchain will play a central role in shaping the future of technology and society.
Read the latest news and announcements in this section.
Read the latest tutorials about payment service providers in this section.
You can access full guides and tutorial to use EZDEX services in this section.
Step by step tutorials and photo guides are available in this section.
Access the latest information about financial and economical matters in Turkey in this section.
Access the latest information about financial and economical matters in UAE in this section.
Explore expert guides, tips, and strategies for understanding and working with gold. Learn everything from basics to advanced knowledge.