What Are Stablecoins? How They Work and Why They Matter in Crypto

Whether you’re a trader hedging against price swings or exploring decentralized finance (DeFi), stablecoins bridge the gap between traditional fiat currencies and digital assets. In this guide, we’ll explain what stablecoins are, how they work, their types, benefits, risks, and why they’re essential for crypto investors. Ready to dive in? Let’s explore!
Table of Contents
What Is a Stablecoin?
A stablecoin is a cryptocurrency designed to maintain a stable value, typically pegged to assets like fiat currencies (e.g., USD) or commodities (e.g., gold).
Unlike volatile cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, stablecoins aim to provide a reliable store of value and medium of exchange, making them ideal for trading, payments, and DeFi applications.
Stablecoins achieve stability through mechanisms like asset reserves or algorithms, ensuring their value remains consistent. This makes them a go-to choice for investors seeking cryptocurrency stability without exiting the crypto market.

Types of Stablecoins Explained
Stablecoins come in various forms, each with unique mechanisms to maintain stability. Here’s a breakdown of the main types:
Fiat-Collateralized Stablecoins
Backed by fiat currencies like USD or EUR, these stablecoins hold an equivalent amount of fiat in reserve for every coin issued. Examples include:
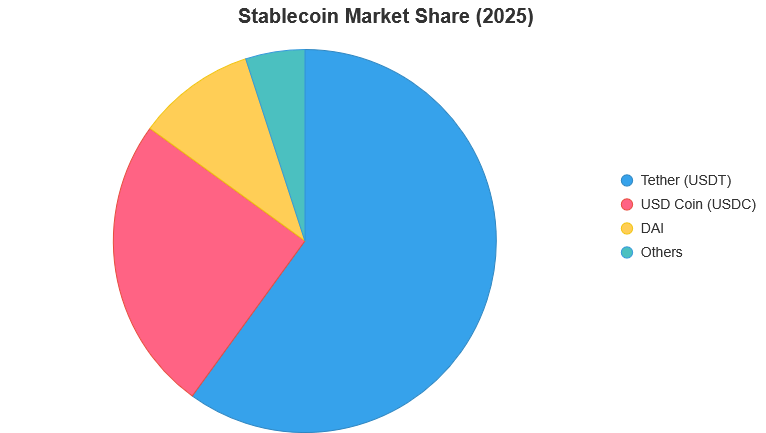
Tether (USDT): Pegged to the USD, widely used for trading.
USD Coin (USDC): Backed by audited USD reserves, popular in DeFi.
💡Why use them? They’re highly stable due to direct fiat backing but rely on the issuer’s reserve management.
Crypto-Collateralized Stablecoins
These are backed by other cryptocurrencies, often over-collateralized to account for volatility. A key example is:
DAI: Pegged to USD but backed by Ethereum, managed by the MakerDAO protocol.
💡Why use them? They’re decentralized, reducing reliance on centralized issuers, but they carry higher volatility risks.
Algorithmic Stablecoins
These rely on algorithms and smart contracts to adjust supply and maintain value, with no physical reserves. An example is:
TerraUSD (UST): Famously depegged in 2022, causing market disruption.
💡Why use them? They’re fully decentralized but risk instability if algorithms fail.
Commodity-Collateralized Stablecoins
Backed by physical assets like gold or silver, these tie their value to commodities. For example:
Digix Gold (DGX): Each token represents a gram of gold.
💡Why use them? They offer exposure to commodities within the crypto ecosystem.
| Type | Backing | Example | Pros | Cons |
| Fiat-Collateralized | Fiat currencies | USDT,USDC | High stability, widely used | Centralized, counterparty risk |
| Crypto-Collateralized | Cryptocurencies | DAI | Decentralized, transparent | Volatility risk |
| Algorithmic | Algorithms | TerraUSD | Fully decentralized | Risk of depegging |
| Commodity-Collateralized | Commodities | DGX | Commodity exposure | Storage and audit challenges |
How Do Stablecoins Work?
Stablecoins maintain their peg through different mechanisms:
- Fiat-Collateralized: Issuers hold fiat reserves (e.g., USD) in a 1:1 ratio, ensuring each stablecoin is redeemable for its pegged value. For example, 1 USDC = 1 USD.
- Crypto-Collateralized: Over-collateralized with crypto (e.g., Ethereum) to absorb price fluctuations. DAI, for instance, uses smart contracts to manage collateral.
- Algorithmic: Smart contracts adjust the coin’s supply based on market demand. If the price rises, more coins are minted; if it falls, supply is reduced.
- Commodity-Collateralized: Backed by physical assets like gold, held in secure vaults and audited regularly.
Why Are Stablecoins Important?
Stablecoins serve several essential functions in the cryptocurrency ecosystem:
- Facilitating Trade: Stablecoins provide a stable medium of exchange, allowing traders to move in and out of volatile cryptocurrency positions without converting to fiat currency. Traders often buy Tether (USDT) or other stablecoins primarily to hedge against the volatility of the cryptocurrency market. By converting their volatile assets into stablecoins, traders can protect their portfolio's value during periods of market uncertainty or downturns without needing to exit the cryptocurrency market entirely. Another key reason traders use stablecoins is for liquidity and ease of movement between exchanges.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): In the rapidly growing DeFi space, stablecoins are used as a reliable store of value and collateral for loans, yield farming, and other financial services.
- Cross-Border Transactions: Stablecoins enable fast, low-cost international payments without the volatility typically associated with cryptocurrencies.
- Financial Inclusion: In regions with unstable fiat currencies, stablecoins offer a safer alternative, allowing people to protect their wealth from inflation and economic instability. For example, to buy and sell tether in Istanbul helps people protect their wealth from Turkish Lira instability.
Are Stablecoins Risky?
While stablecoins offer many advantages, they are not without risks. Here is a list of most common ones.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: As stablecoins gain popularity, they have come under increased scrutiny from regulators worldwide. There is uncertainty about how they will be regulated in the future.
- Counterparty Risk: For fiat-collateralized stablecoins, the stability of the stablecoin relies on the issuer’s ability to hold the necessary reserves. If the issuer fails to maintain the reserves, the stablecoin could lose its peg.
- Market Risks: Algorithmic stablecoins, in particular, are vulnerable to market dynamics. If the algorithms fail to maintain the peg, the stablecoin could experience significant price fluctuations.
The Future of Stablecoins
Stablecoins are poised to shape the future of finance. As DeFi grows and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) emerge, stablecoins could become a cornerstone of global payments and investments. However, their success depends on regulatory clarity and technological advancements.
Ready to explore stablecoins? Sign up for EZDEX to trade USDT, USDC, and more, or check out our stablecoin tutorials for step-by-step guides.
Share your thoughts in the comments below and earn EZGEM rewards!
Read the latest news and announcements in this section.
Read the latest tutorials about payment service providers in this section.
You can access full guides and tutorial to use EZDEX services in this section.
Step by step tutorials and photo guides are available in this section.
Access the latest information about financial and economical matters in Turkey in this section.
Access the latest information about financial and economical matters in UAE in this section.
Explore expert guides, tips, and strategies for understanding and working with gold. Learn everything from basics to advanced knowledge.